Abstract
Introduction: TP53 aberrations, including mutations and deletion of 17p (del17p), are important adverse prognostic markers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Prevalence of TP53 aberrations ranges from 7-11% in untreated CLL and increases with disease progression and treatment. Among CLL patients with TP53 aberrations, co-occurrence of TP53 mutations with del(17p) is common. CLL patients with TP53 mutations or del(17p) have significantly worse outcomes when compared to wild-type patients. Previous studies, focusing on CLL patients at time of treatment, are mixed as to whether a single or more than one TP53 aberration impacts outcomes. TP53 is less well studied in monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL), an asymptomatic pre-malignant state of CLL. Del(17p) occurs in 3-4% of MBL individuals, and a study of 54 MBL individuals reported a 2% mutation frequency in TP53. Here we estimated prevalence and evaluated the impact of TP53 aberrations in a large cohort MBL or untreated CLL individuals.
Methods : Patients with CLL or MBL diagnosed between 2000 and 2019 from the Mayo Clinic CLL Resource with pre-treatment peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) collected within two years of diagnosis were considered. DNA was extracted from PBMCs with purity >80% or with sorted CD5+/CD19+ clonal cells. The entire coding regions of 59 CLL driver genes were paired end sequenced. Median coverage depth was >1000x per nucleotide, allowing for detection of mutations with variant allelic fraction (VAF) as low as 1%. Somatic mutations were called using MuTect2 in tumor-only mode, and high impact mutations (frameshift, nonsense, and splicing variants) and missense mutations in CLL hot spots were selected.
Somatic mutations and FISH del(17p) were used to define TP53 state for each patient: 1) wild-type [no TP53 mutations and normal del(17p)], 2) single-hit [one TP53 mutation or del(17p)], or 3) multi-hit [multiple TP53 mutations or TP53 mutation and del(17p)].
Time to first treatment (TTFT) and overall survival (OS) were analyzed by TP53 state. TTFT and OS were defined as time from sample collection to first treatment or death, respectively, or last follow-up date. Median TTFT and OS was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method. We used Cox regression to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals for TTFT and OS associations. The models were adjusted for known adverse prognostic factors including clinical diagnosis (CLL or MBL), age at diagnosis, Rai stage, b2 microglobulin, and IGHV mutation status.
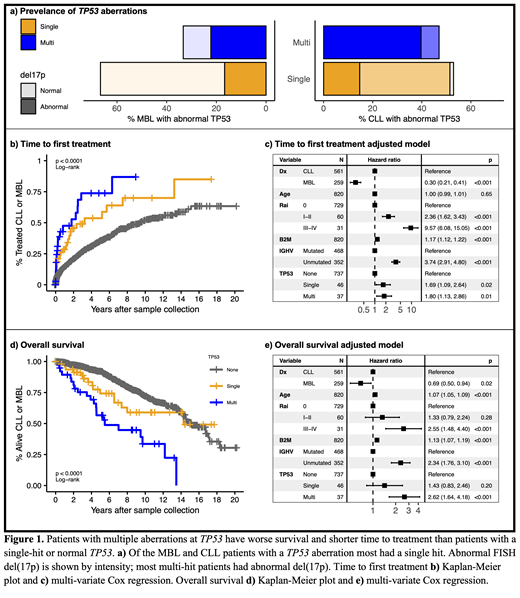
Results: Individuals with CLL (N=597) or MBL (N=285) were analyzed for prevalence of TP53 mutations and del(17p). We found 58 CLL patients (9.7%) and 15 MBL individuals (5.3%) had TP53 mutations. The median VAF in CLL was 30.9% (<10% VAF, n=21) and in MBL was 13.5% (<10% VAF, n=7). Del(17p) was present in 37 patients with CLL (6.2%) and 7 individuals with MBL (2.7%). In total, 86 CLL/MBL patients had a TP53 mutation and/or del(17p): 56.8% (48 patients) were single-hit and 44.2% (38 patients) were multi-hit (Fig. 1a).
Patients with any TP53 aberration had shorter TTFT than wild-type patients (median 2.3 vs 9.4 years). Among patients with TP53 aberrations, median TTFT was shorter in multi-hit patients (20 events, 1.8 years) compared to single-hit patients (24 events, 3.2 years) (Fig. 1b). In Cox regression, single-hit (HR = 1.7 [1.1-2.6]) and multi-hit (HR = 1.8 [1.1-2.9]) patients had shorter TTFT compared to wild-type patients after adjusting for covariates (Fig. 1c).
Multi-hit patients also had shorter OS compared to wild-type patients, while OS in single-hit patients did not significantly differ from wild-type patients (Fig. 1d). Median OS was 5.5 years in multi-hit patients (22 deaths) compared to 15.1 years in wild-type patients (196 deaths) and 14.3 years in single-hit patients (15 deaths). In the OS model adjusted for covariates, multi-hit patients had a significant increased risk (HR = 2.6 [1.6-4.1]), but single-hit patients did not (HR = 1.4 [0.8-2.5]) compared with wild-type patients (Fig. 1e). OS HRs remained stable after censoring at time of treatment. Both TTFT and OS HRs were consistent when mutations with VAF < 10% were excluded.
Conclusions: This study suggests single versus multi-hit TP53 aberrations may be important for prognostic outcomes in untreated CLL and MBL patients. Prognostic metrics may need to consider single versus multi-hit TP53 aberrations and include TP53 mutations with low VAF.
Cerhan: Regeneron Genetics Center: Other: Research Collaboration; Celgene/BMS: Other: Connect Lymphoma Scientific Steering Committee, Research Funding; NanoString: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Parikh: Pharmacyclics, MorphoSys, Janssen, AstraZeneca, TG Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, AbbVie, and Ascentage Pharma: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Verastem Oncology, and AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kay: MEI Pharma: Research Funding; Bristol Meyer Squib: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Dava Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Tolero Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios Pharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Targeted Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CytomX Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Behring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sunesis: Research Funding; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Oncotracker: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Morpho-sys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Rigel: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal